
PhDr. Ingrid Palaščáková Špringrová, Ph.D.
Acral coactivation therapy – ACT
The beginnings of the ACT method date back to 1991 when I was often working with patients after spine surgeries during my practice in the National rehabilitation centre Kováčová (Slovakia). For the therapy of these muscles, we often used the exercises of Roswitha Brunkow whose contribution to physiotherapy as well as many modern procedures remains often neglected.
When I founded the rehabilitation centre REHASPRING in 2006, frequent questions of patients were aimed at the need of an effective and understandable autotherapy. A method based on the system of supports started to develop step by step. Long-time testing in practice, evaluation of patients and therapy success led finally in an uncomplicated system of treatment called the Acral coactivation therapy.
Motor learning
The basic target of ACT is to rehabilitate our wrong movement habits by means of motor learning. In spite of the fact that motor learning is a conscious process (it proceeds at the level of cerebral cortex), it is possible to reach for its assumption by repeating exercises. For a successful fixation of a new/changed way of movement performance, numerous repetitions are necessary – some studies state around 2 000 repetitions.

Motor development of children

Sets of ACT exercises use positions of an early motor development which we have all experienced. During adolescence, the range and variety of our movement skills adapt to our environment and its requirements – whether negatively or favourably. For that reason, the ACT method is not only a therapeutic tool but it also enriches our motor skills by these often forgotten patterns.
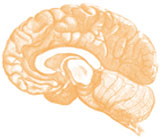
Press exercises against acral parts
Press exercises against acral parts of limbs are used during the ACT exercises. For purpose of the therapy, we define primarily two types of acral parts:
- Upper extremity – hand (from a wrist to fingertips).
- Lower extremity – foot (from a heel up to toes).
Press exercises against acral parts are performed for real or virtually. The preferred real press exercise is a physical press exercise against acral parts towards segments of own body, eventually towards the surroundings (table, floor, wall, etc.) In case it is not possible to apply real press, we use the virtual press which we perform against an imaginary obstruction and it serves mainly for a better visualization of direction and for the press intensity.
Except for press exercises against acral parts, also the arching of acral parts influences the effectiveness of exercises. It is necessary to keep the arching during exercises. Non-keeping of the arching during press exercises shows itself as flat hands (hyperextension of fingers) on hands and flat feet (hyperextension of fingers) on feet.
Spine straightening
Thanks to its emphasis on spine straightening, the ACT method represents an effective therapy for many disorders of the movement apparatus – from frequent functional and degenerative states of spine up to very specific diseases.
In the ACT therapy, we reach the spine straightening by the coactivation of ventral and dorsal muscular chains which are activated by the usage of acral parts during the press exercises. Correct loading and press exercises against acral parts “start” the movement pattern leading to the spine straightening. A qualitative correction of these movement patterns proceeds already consciously and the occurrence of motor mistakes minimizes by repeating.
Based on this principle, the ACT exercises straighten our spine, strengthen dorsal muscles, compensate dysbalances and consequently stabilize the entire movement apparatus. What’s more, regarding the fact that press exercises in the ACT method can activate also deeper muscles of the body, it is possible to use the therapy also for the strengthening of expiratory muscles and improve so their function.



ACT – Autotherapy
A therapist trained in the ACT method is competent to analyse motor mistakes of patients and is able to offer them a very individual program of autotherapy. Patients learn to perform ACT exercises and their versions after a professional training.
At the same time, they find out which everyday actions they can enrich by ACT elements and intensify so the effect of therapy. By means of tiny changes, cleaning, working at the computer or in the garden can become activities with a strong therapeutic potential.
